Phishing is a type of cyberattack that involves tricking victims into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial information. Phishing attacks can be particularly dangerous because they can be difficult to detect and can easily result in the theft of valuable information. Two-factor authentication (2FA) has become a popular tool for protecting against phishing attacks, but as security professionals have discovered, 2FA is not foolproof.
While many organizations rely on 2FA to protect against common schemes like credential stealing or login theft, hackers have found multiple ways to intercept 2FA and use it to facilitate phishing attacks. In fact, there are even public tools available that make it easier for less experienced phishers to accomplish successful phishing attacks against 2FA.
One way that hackers can bypass 2FA is through the use of man-in-the-browser (MitB) attacks. These attacks involve using browser extensions to scrape or sell data, including second factor login information. By installing a browser extension that has access to the complete canvas of the browser, hackers can monitor a user's session and capture everything that is being rendered on the screen, including sensitive information entered during a 2FA login.
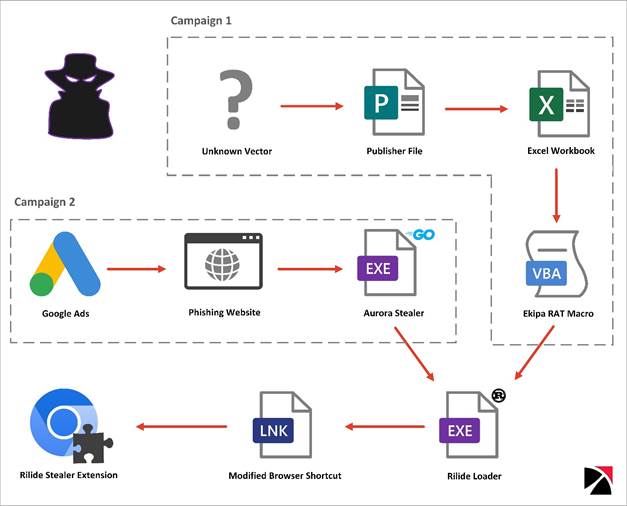 |
| Figure 1. Infection Chains Leading, image trustwave |
Technical support scams are another way that hackers can get around 2FA security protocols. In this type of phishing scheme, scammers convince users to install remote access software, such as TeamViewer or LogMeIn, under the guise of technical support. Once installed, the software provides a backdoor into the victim's device, which can be sold on the Dark Web to other bad actors. Even the best antivirus software may not be able to detect this type of backdoor, and 2FA will not prevent the phishing scheme from succeeding.
Another tactic used by phishers is to create fake 2FA pages or pop-ups that closely resemble legitimate authentication websites. Unsuspecting users are presented with a login experience that appears to be their normal 2FA process, but is actually a fake site that captures their authentication codes and user credentials. The phisher can then use this data to access one or more corporate systems.
Scareware is another way that phishers can obtain the credentials they need to subvert 2FA solutions. This tactic involves using security alerts that appear to come from legitimate providers to trick users into resetting their passwords due to a supposed security threat or breach. This type of scareware has been used to successfully bypass 2FA security protocols and gain access to sensitive information.
While 2FA and multi-factor authentication (MFA) can be effective tools for protecting against unauthorized user logins, they are only part of a layered phishing defense. To stay ahead of phishing attacks, organizations should implement best practices and deploy multiple tools that protect against these attacks in real-time. Employee training is one way to help identify phishing scams, but it is important to recognize that no amount of training will ever be 100% effective against phishing attacks. Conducting a thorough audit of an organization's IT security platform can also help identify vulnerabilities and implement the best security practices to protect against phishing attacks.


0 Comments